Apple (NASDAQ:AAPL) Faces China Struggles, AI Expansion, and Market Shifts—Is It a Buy?
Apple’s (NASDAQ:AAPL) China Problem: How Bad Is It?
Apple’s (NASDAQ:AAPL) presence in China has been a pillar of its global strategy for years, but recent sales data show a serious problem. Apple’s revenue from Greater China dropped to 14.8% of total sales in Q1 2025, down from 17.4% in Q1 2024 and 20.4% in Q1 2023. This downward trend isn’t random—it’s directly tied to the rise of Huawei and other domestic competitors, regulatory challenges, and Apple’s struggles with AI integration in China.
China’s overall smartphone market has recovered by 4% year-over-year, reaching 285 million units sold in 2024, but Apple has been losing share. Huawei, fueled by strong government support and its advanced Mate 60 Pro, saw 37% growth in shipments, while Apple was forced to offer rare discounts of up to 500 yuan ($70) to retain market share. Canalys reported that Apple’s Q4 2024 iPhone shipments in China fell by 25%, a major blow to its dominance.
Why Did Apple Choose Alibaba Over Baidu for AI in China?
Apple can’t directly introduce Apple Intelligence in China due to strict regulatory constraints. Instead, it must partner with domestic AI providers to integrate features into its ecosystem. Apple chose Alibaba’s Qwen AI model over Baidu (BIDU) or DeepSeek, a decision driven by Alibaba’s dominance in AI rankings and its ability to meet Apple’s high security and compliance standards.
The Qwen-VL model is currently the top-ranked open-source AI model in China, outperforming Meta’s Llama and training over 90,000 derivative models. With AI integration missing from China’s iPhone lineup, over 50% of Chinese iPhone users surveyed cited the AI delay as their primary reason for not upgrading. Apple’s AI partnership with Alibaba is expected to roll out later in mid-2025, which could stabilize Chinese sales if executed effectively.
U.S. Market Still Strong: Will It Be Enough?
While China presents a challenge, Apple’s home market remains resilient. The iPhone 16 lineup is expected to drive strong demand in the U.S., especially with the rumored addition of Apple’s in-house AI models for users outside China. Services revenue—Apple’s highest-margin segment at 75% gross margins—continues to grow at double-digit rates, mitigating some of the impact of slowing iPhone sales.
Apple’s upcoming low-cost iPhone SE 4 is set to launch in March 2025, featuring Face ID and a larger screen similar to the iPhone 14. This could help Apple capture price-sensitive consumers, particularly in emerging markets where its premium models struggle to compete.
Stock Performance: Is Apple Still a Buy?
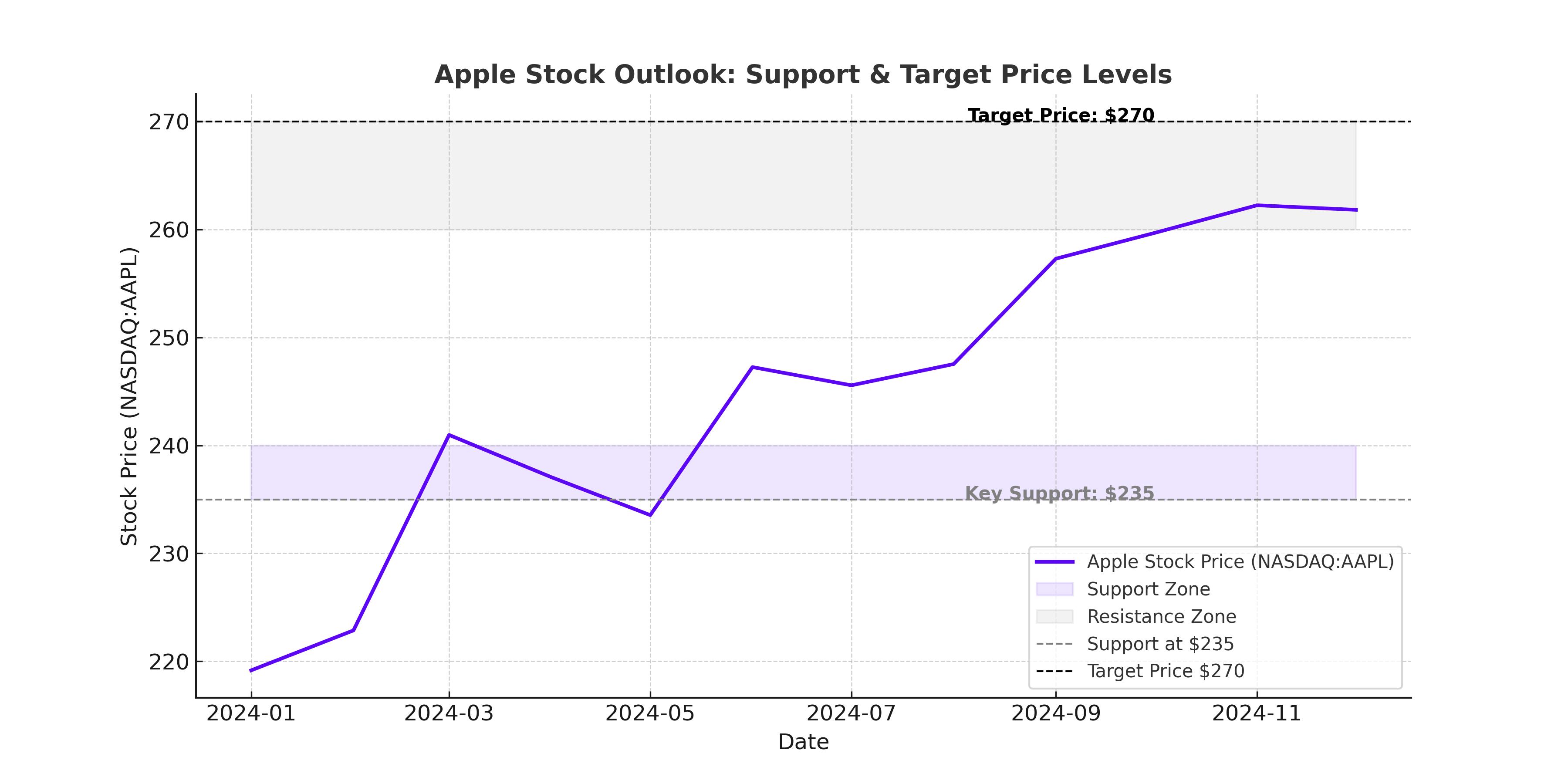
Apple’s stock price is down 2% year-to-date, underperforming the S&P 500. However, over the past 12 months, AAPL is up 34%, driven by investor confidence in its AI roadmap, services expansion, and strong U.S. demand.
The stock is currently trading at $244 with a market cap of $3.67 trillion. Analysts have raised their price targets over the past three months, with the median target at $254 and the mean at $250. Despite recent struggles, Apple’s forward P/E ratio of 33.2 still trades at a premium to the sector median of 25.3, reflecting investor expectations for long-term growth.
Is Apple’s AI Expansion Enough to Counter Weak China Sales?
Apple has historically been a late mover in AI, choosing to integrate rather than build from scratch. Its partnership with OpenAI for AI-powered Siri upgrades and its expansion into personal AI assistants give it an advantage over competitors who have been burning cash on massive AI compute investments. However, Apple still lags behind rivals like Google in cloud-based AI capabilities, which could be a concern for long-term investors.
Apple’s long-term AI strategy includes humanoid robotics, a space where Tesla (TSLA) and Meta (META) are already investing heavily. Apple’s massive ecosystem of 2.35 billion active devices gives it a huge edge if it successfully integrates AI-powered robotics into consumer applications.
Apple’s (NASDAQ:AAPL) Revenue Breakdown: Where Does the Growth Come From?
Apple’s revenue remains heavily dependent on iPhone sales (56%), followed by services (21.2%), wearables (9.4%), Mac (7%), and iPad (6.5%). The iPhone business remains Apple’s biggest cash cow, but services growth is the primary driver of margin expansion.
Key Financial Metrics:
- iPhone Sales in China: Down 25% in Q4 2024
- Apple’s Gross Margin: 43.5% (up from 42.3% in Q1 2024)
- Services Revenue Growth: 14% year-over-year
- Cash Reserves: $53 billion, with a focus on AI-related M&A
- Share Buybacks: Apple continues aggressive buybacks, reducing outstanding shares and boosting EPS
What’s Next for Apple?
Apple’s March 2025 Shanghai Developer Conference is expected to unveil its next-generation AI integration, which could bolster Chinese sales if executed correctly. Additionally, Apple’s health technology expansion—including advanced health-tracking wearables and AI-powered diagnostics—could position it as a major player in digital health, further boosting its services revenue.
With tariffs, regulatory pressures, and competitive threats in China, Apple’s long-term success depends on whether it can offset declining iPhone sales with AI innovation, services growth, and expansion into emerging product categories like robotics and health tech.
Buy, Sell, or Hold?
Apple remains a long-term buy, but near-term risks—particularly in China—could lead to continued volatility. Investors looking for short-term gains might find better opportunities elsewhere, but long-term investors should consider accumulating shares on weakness.
For real-time Apple stock updates, check the AAPL chart.
Apple’s ability to navigate AI, services expansion, and China’s competitive landscape will determine whether it can sustain its $3.67 trillion valuation—or push even higher.